Reportar esta entrada
Más sobre la misma comunidad-colección
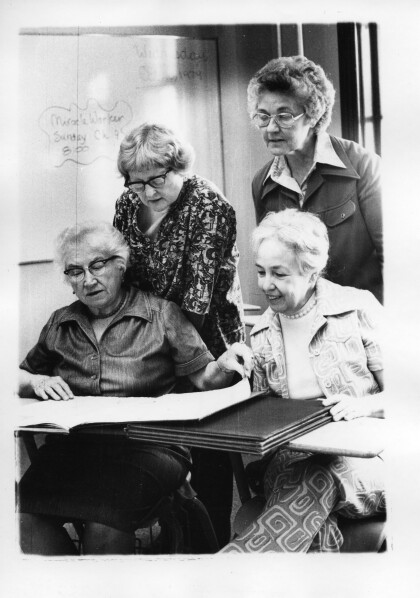
Helen Saunders, Virginia Driscoll, Rose McIntrye, Bernice Juen
Sisters Helen Saunders, Virginia Ann Driscoll, Rose Anthony ...
Loretto Middle School Students - El Paso, Texas
Students at Loretto Middle School 1980-1989 - El Paso, Texas.
Loretto Student performing a dance
Loretto student at a recital - Cielo Vista Mall during the years ...
Herminia and Ray Duran's Wedding Toast
Herminia Cardiel Duran and Ray Duran toast alongside area ...
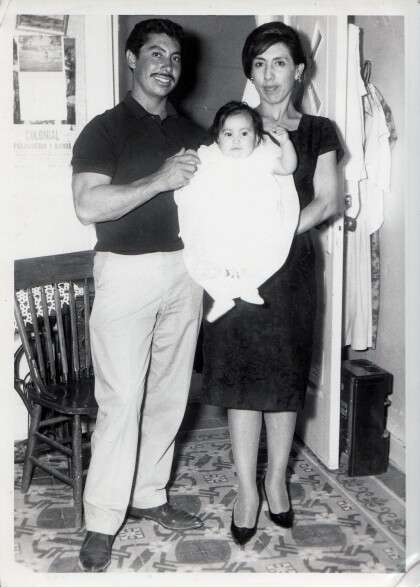
Carmen and Pedro Cardiel holding Herminia Duran
Herminia Duran being held by her aunt and uncle Carmen and Pedro ...
Herminia and Ray Duran's Wedding Toast
Herminia and Ray Duran toast as newlyweds next to Herminia's ...
St. Ignatius' School First Grade Class
St. Ignatius Parish was the third church founded by Padre Pinto ...
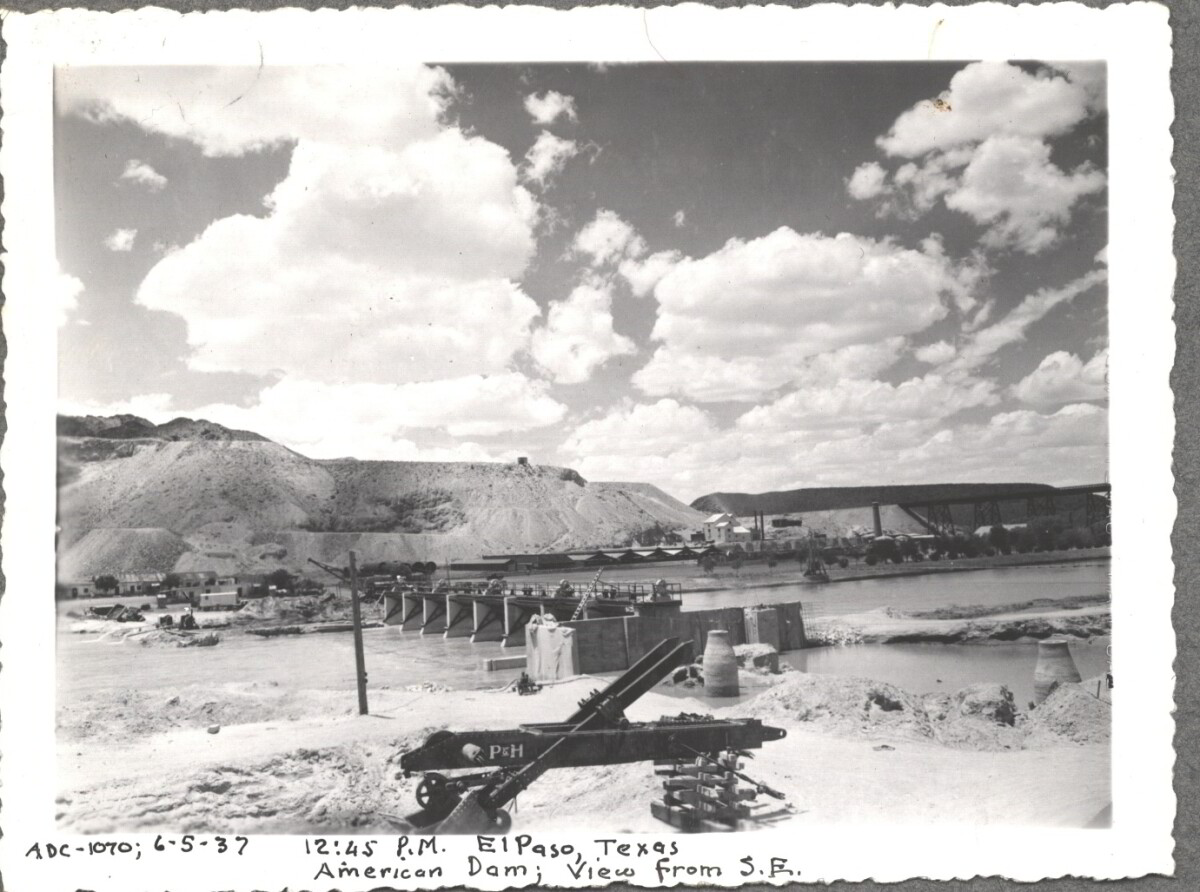
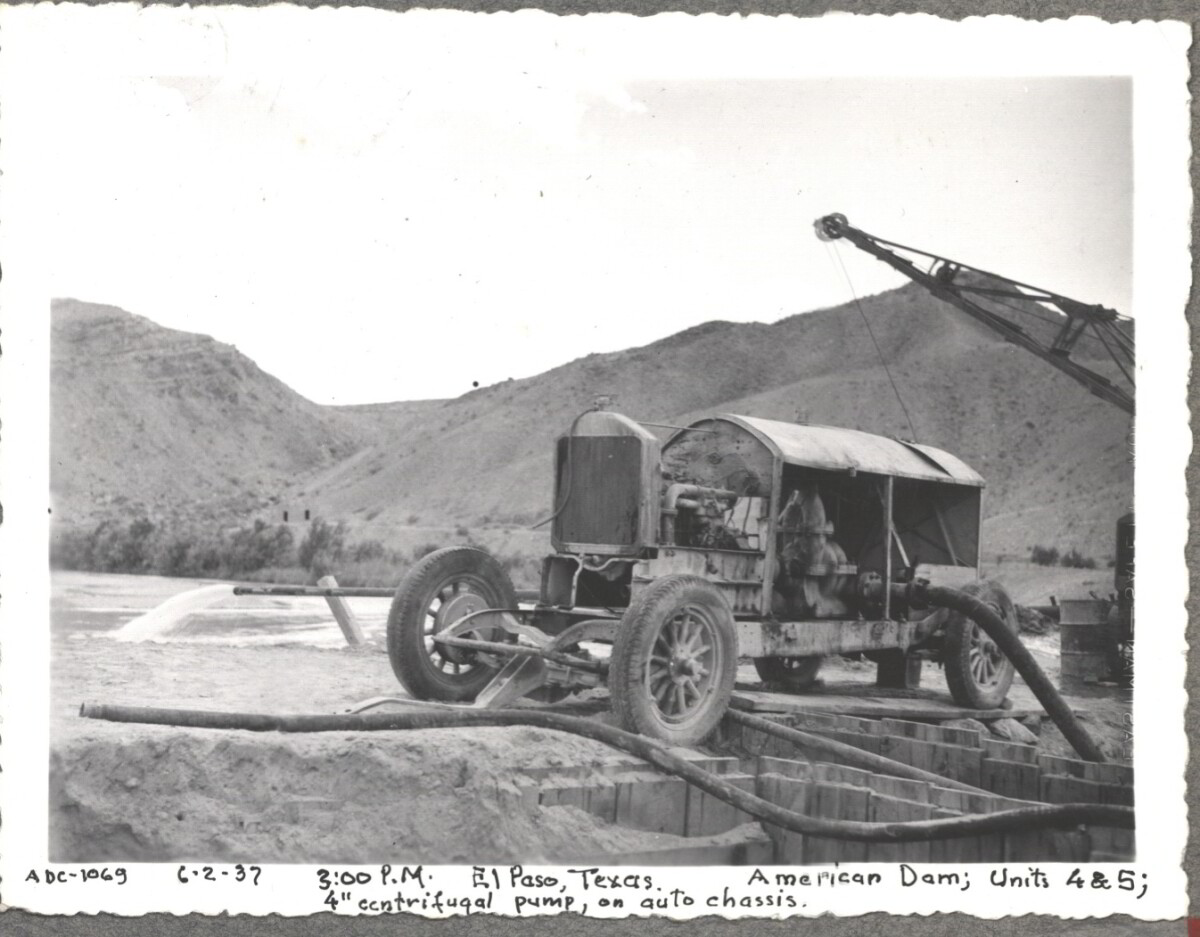
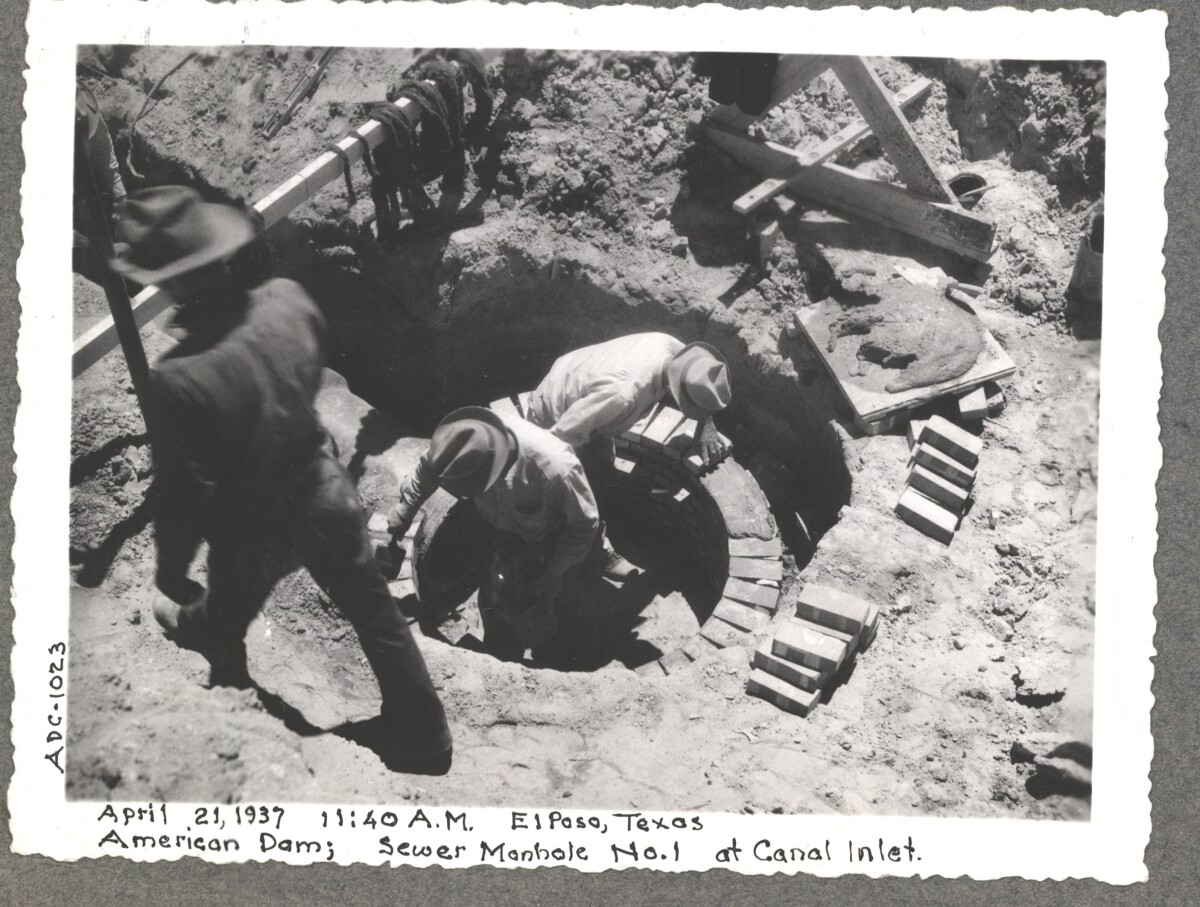
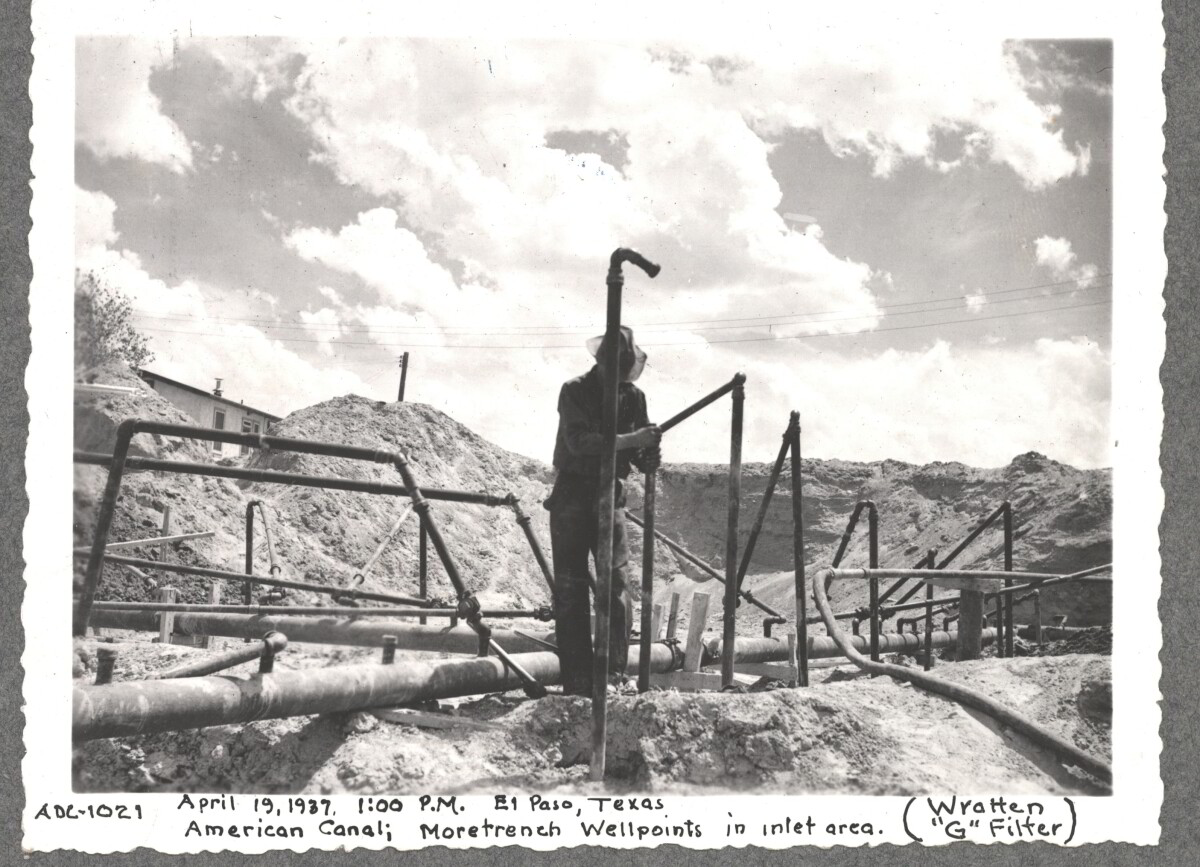
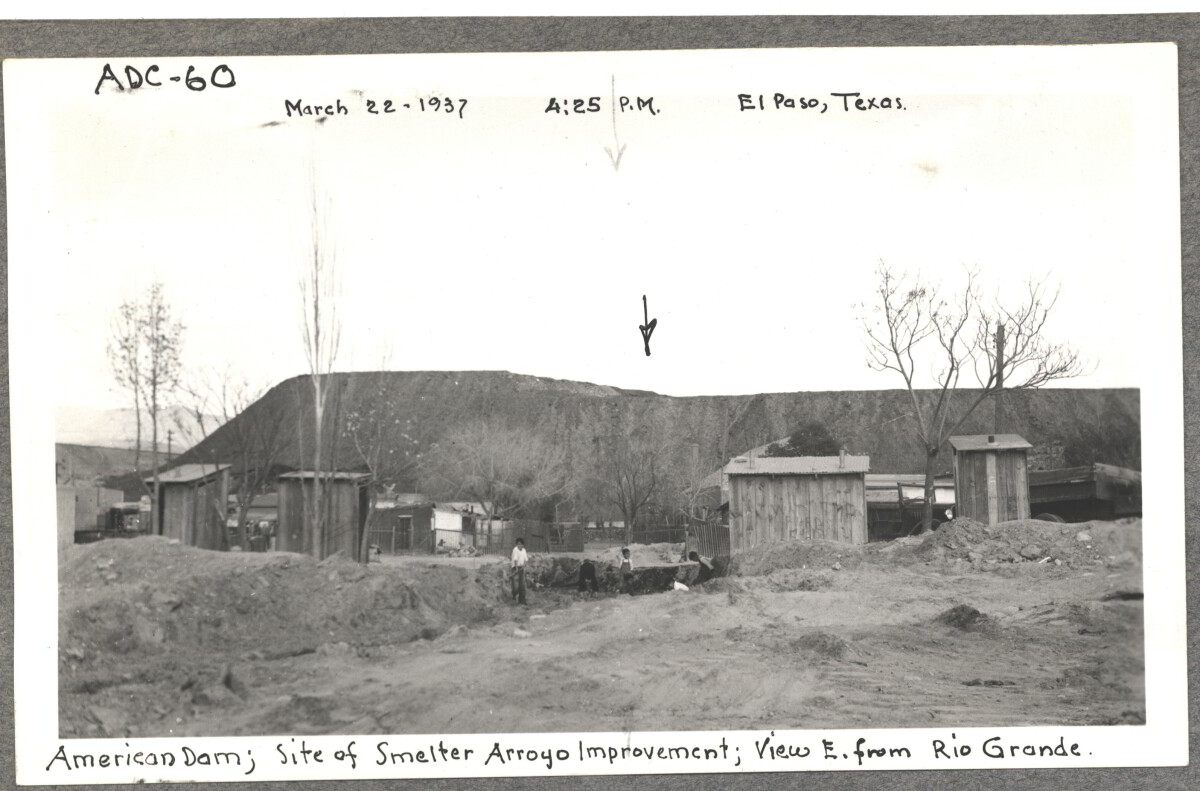
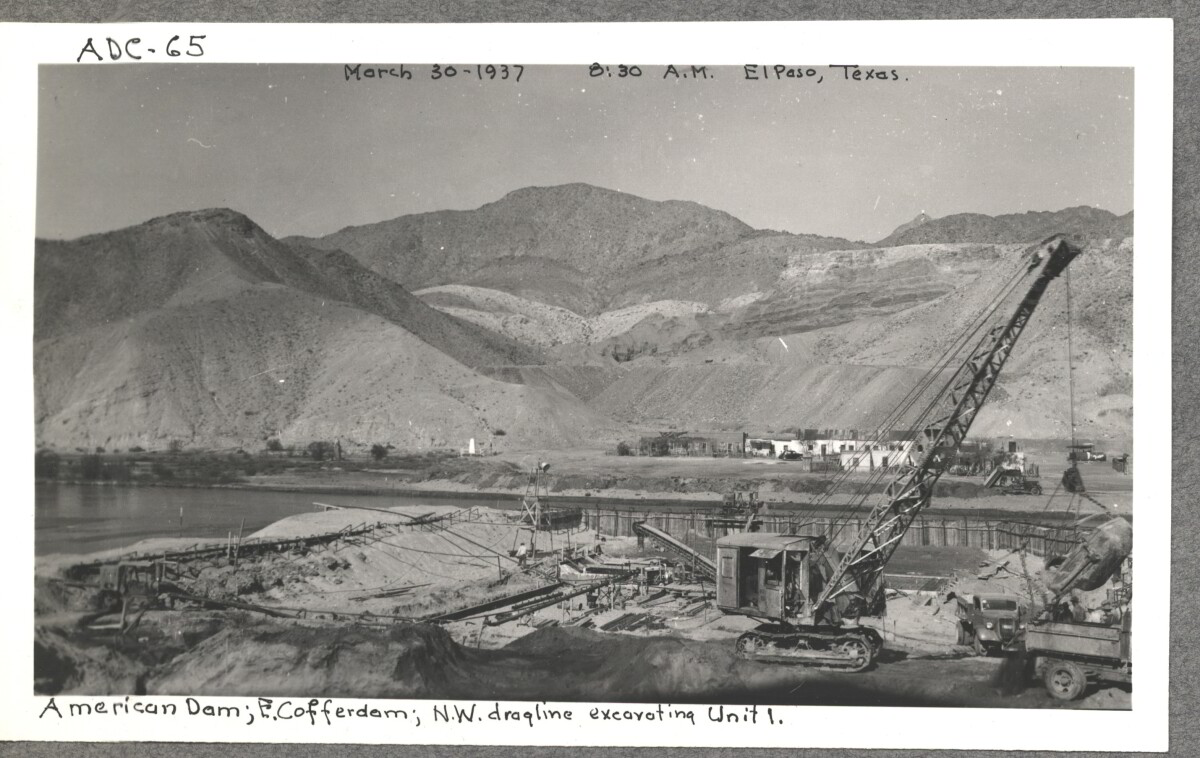
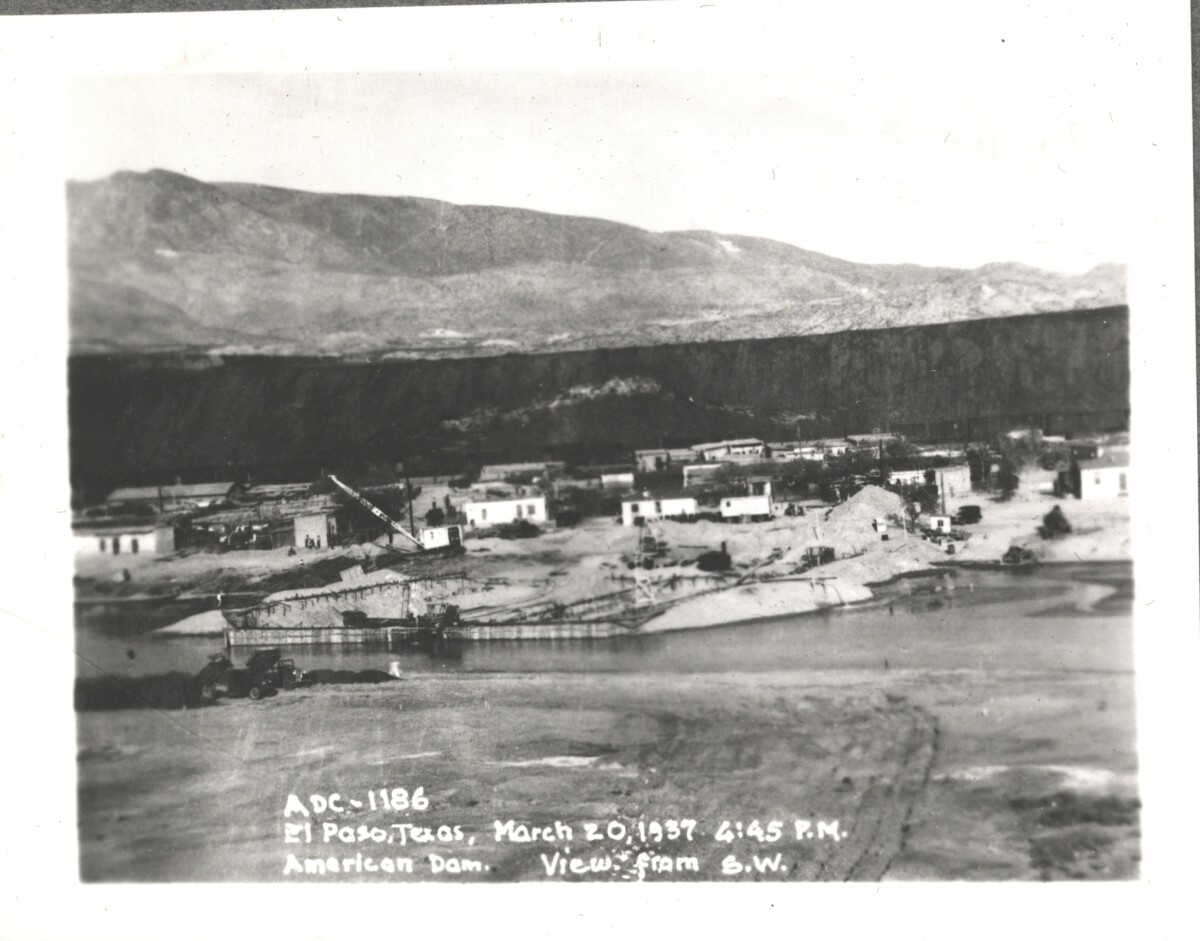
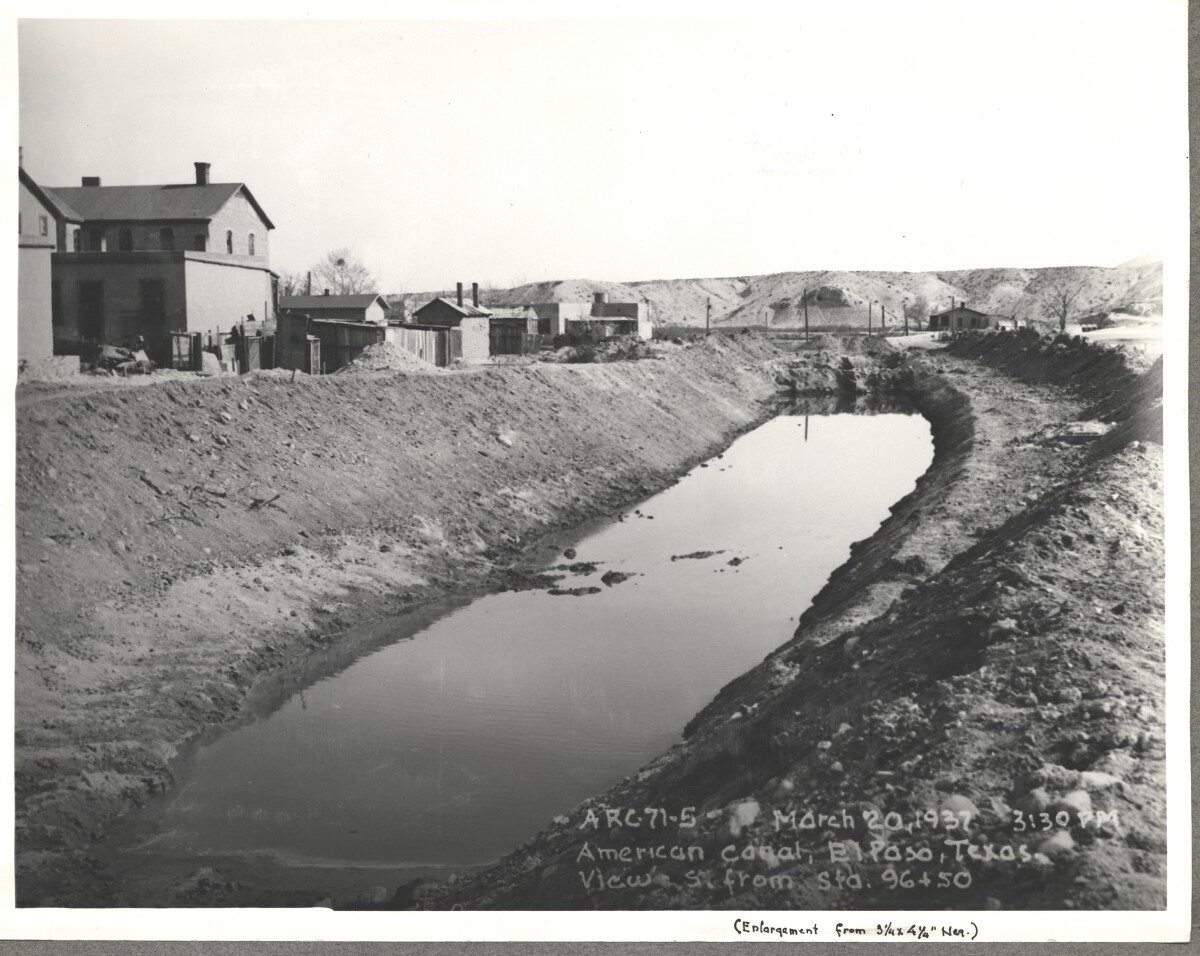

















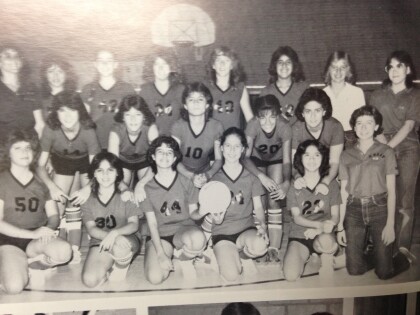





















Comentarios
Hacer un comentario